I will explain how to check the specifications of Windows 11. There are cases where the specifications installed in a Windows 11 PC are checked due to various factors such as heavy operation of Windows 11, when replacing a PC, and the number of supported bits when installing software.
In this article, we will explain how to read the Windows Processor, Installed RAM, System type (checking the number of bits), edition, and version that can be checked in “System”.
The minimum system requirements required to operate Windows 11 are excerpted from the Microsoft official website and described below.
【CPU】
・1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster with 2 or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or System on a Chip (SoC).
【RAM】
・4 gigabyte (GB).
【Storage】
・64 GB or larger storage device Note: See below under “More information on storage space to keep Windows 11 up-to-date” for more details.
引用元: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-11-specifications
In addition, as a supplement, we will also explain how to start the task manager and check resources when the Windows 11 PC feels heavy.
Windows11:PC Spec Confirmation
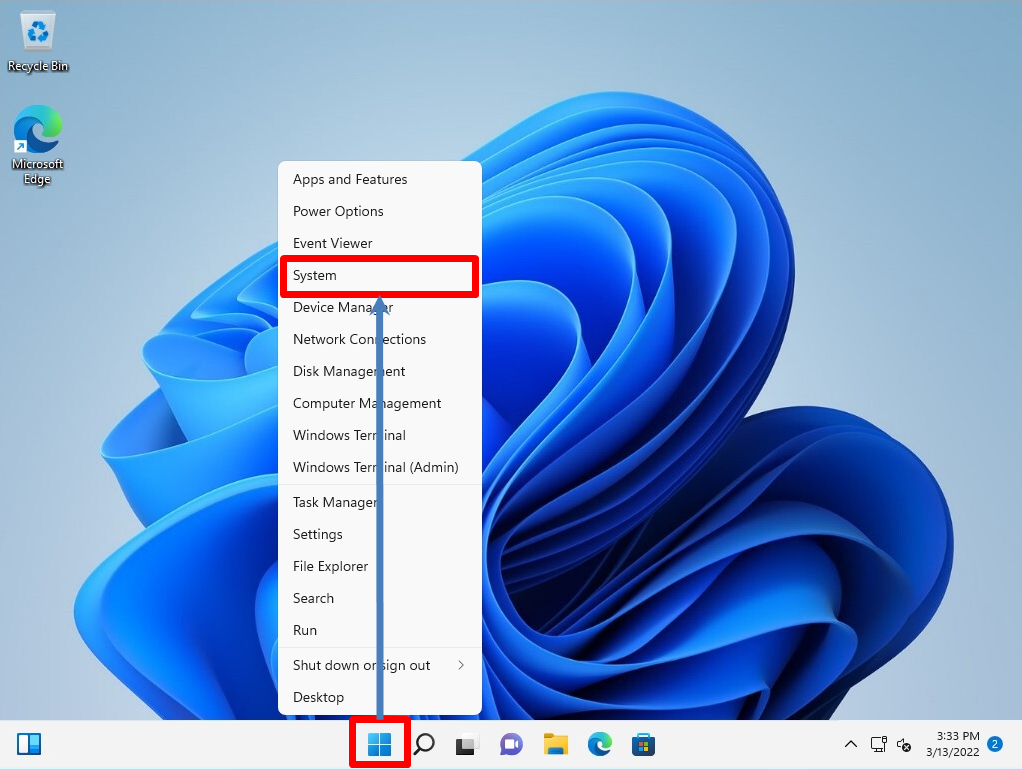
Right-click on the taskbar Windows Mark” -> select System.
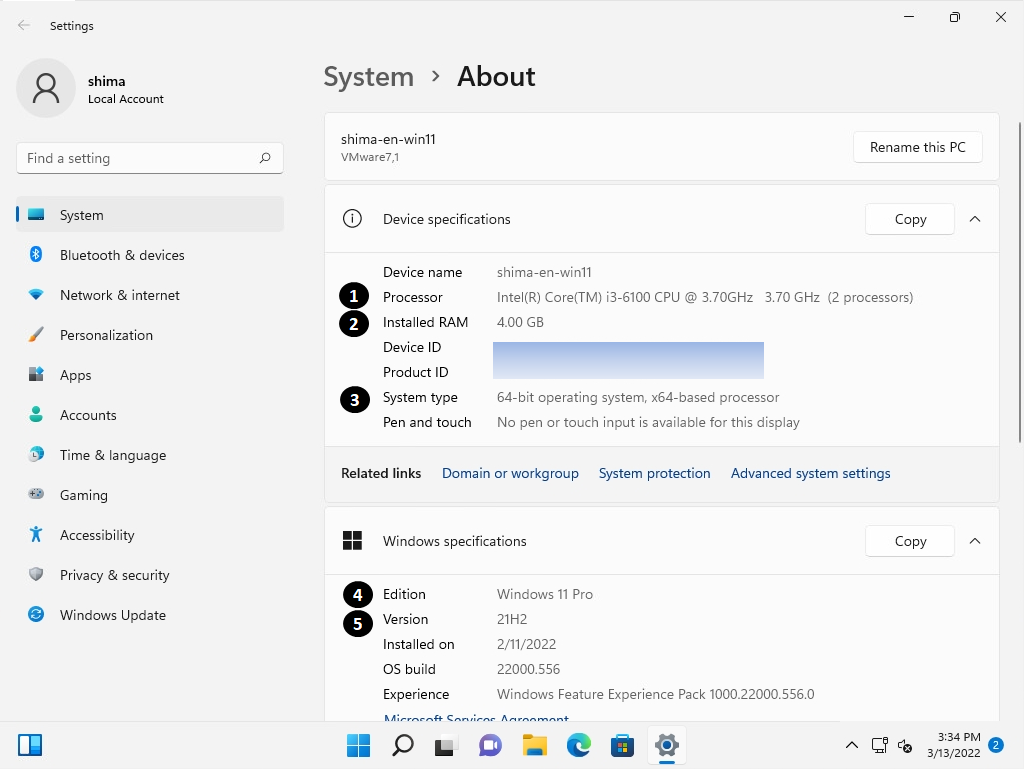
You can check the following ① to ⑤ in “System”.
[Device specifications]
① Processor
② Installed RAM
③ System type: Check the number of bits
[Windows specifications]
④ Edition
⑤ Version
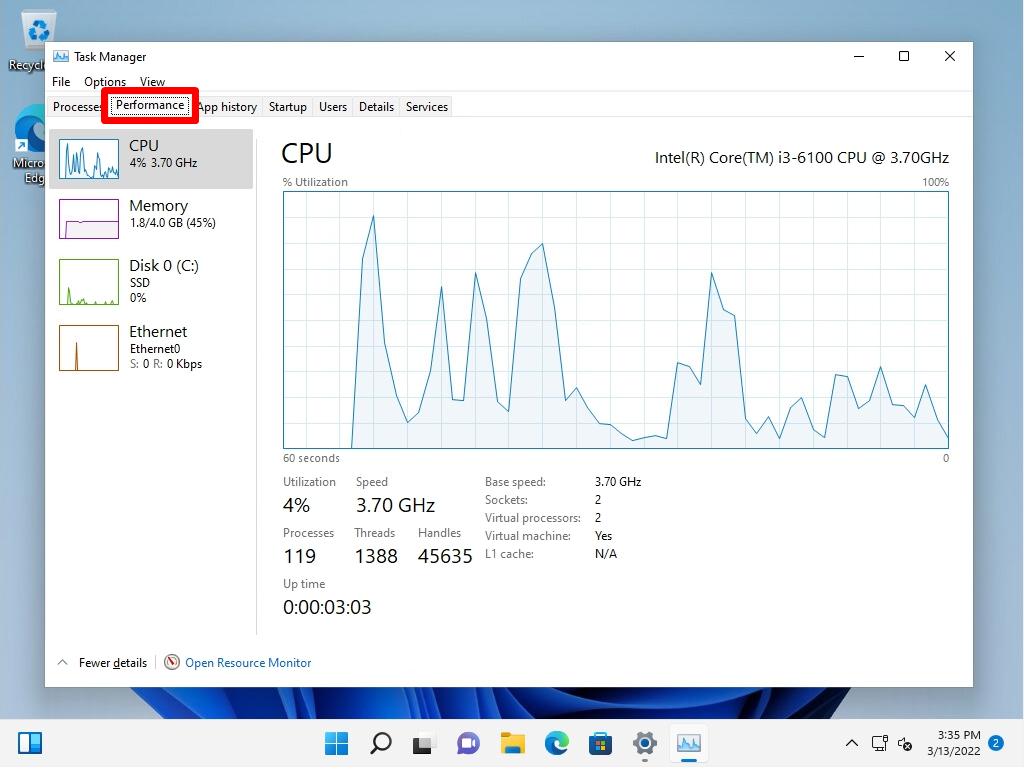
How to check when the operation of Windows 11 PC becomes slow?
If your Windows 11 computer becomes sluggish, you can use the task manager to check how much load is applied to the “CPU”, “Memory”, “Disk”, and “Network”.
“Task Manager” can be started by the shortcut key (control + shift + esc).

You can check the resource information of “CPU”, “Memory”, “Disk”, and “Network” on the “Performance” tab.