Explains how to check the specifications of Windows Server 2016. There are cases where you can check the specifications installed in the Windows Server 2016 server due to various factors such as the heavy server, server replacement, and the number of supported bits when installing software.
Explains how to read the Windows processor, Installed RAM, System type (checking the number of bits), edition, and version that can be checked in.
The minimum system requirements required to operate Windows Server 2016 are excerpted from the official Microsoft website and listed below.
【CPU】
・1.4 GHz 64-bit processor
・Compatible with x64 instruction set
【RAM】
・512 MB (2 GB for servers with the Desktop Experience Server installation option)
【Storage controller and disk space requirements】
・ 32 GB
Quote source:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/get-started/hardware-requirements
In addition, as a supplement, we will also explain how to start the task manager and check resources when the Windows Server 2016 server feels heavy.
Windows Server 2016:Check server specifications
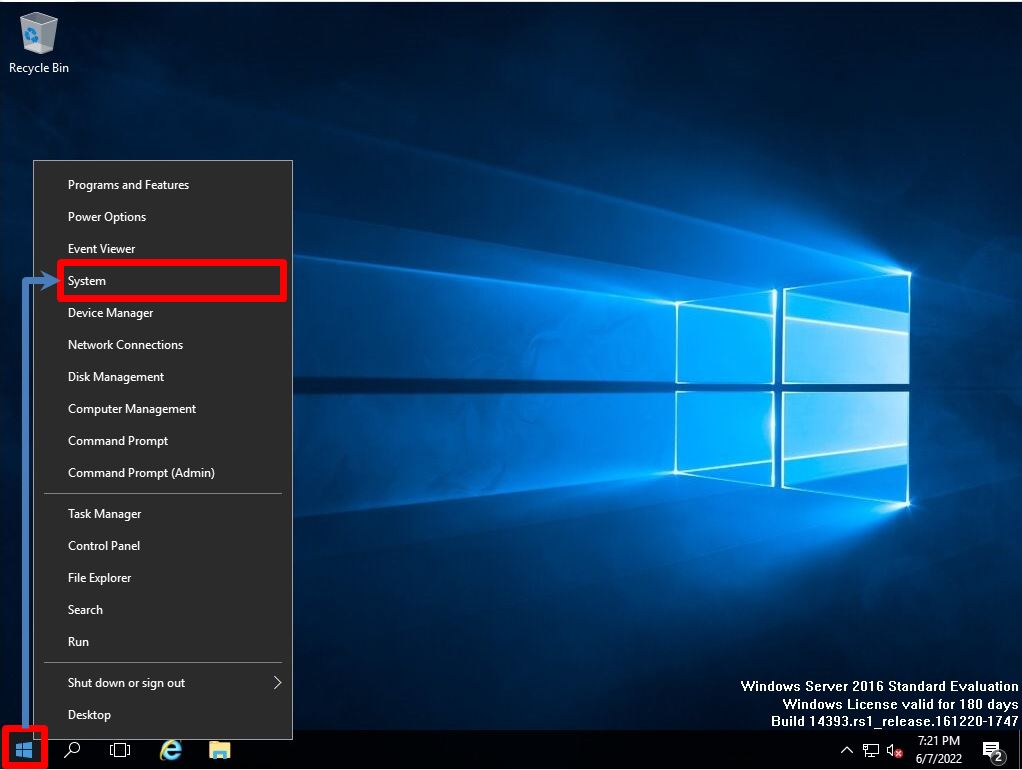
Right-click the Windows mark at the bottom left of the desktop screen –> select System.
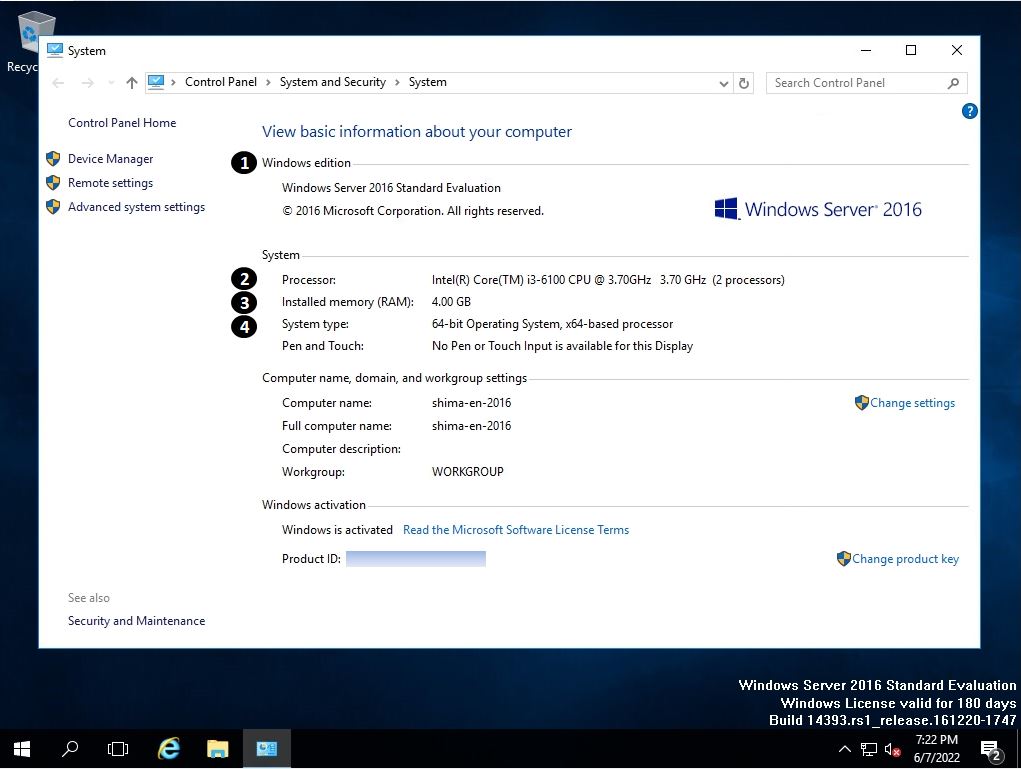
You can check the following① to ④ in “System”.
① Windows edition
② Processor
③ Installed memory (RAM)
④System type: Number of bits
How to check when the operation of Windows Server 2016 becomes heavy?
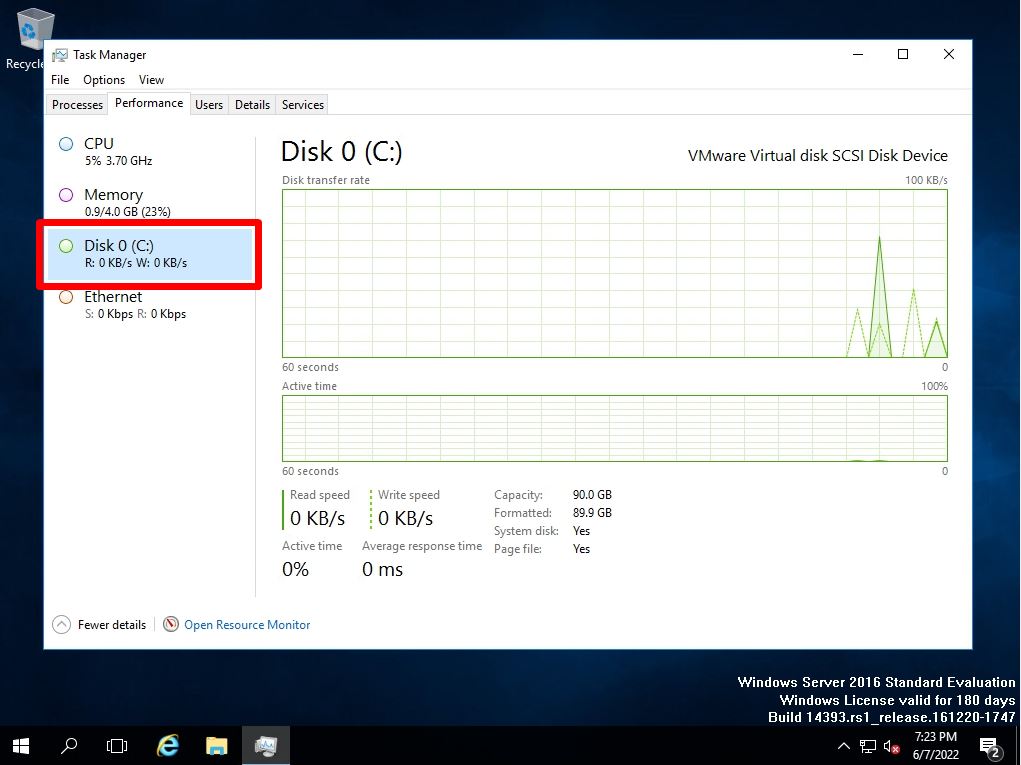
When the operation of Windows Server 2016 becomes heavy, you can check how much load is applied to “CPU”, “Memory”, “Disk”, and “Network” by using Task Manager. Right-click on the part where the taskbar icon is not displayed –> Select “Task Manager”.
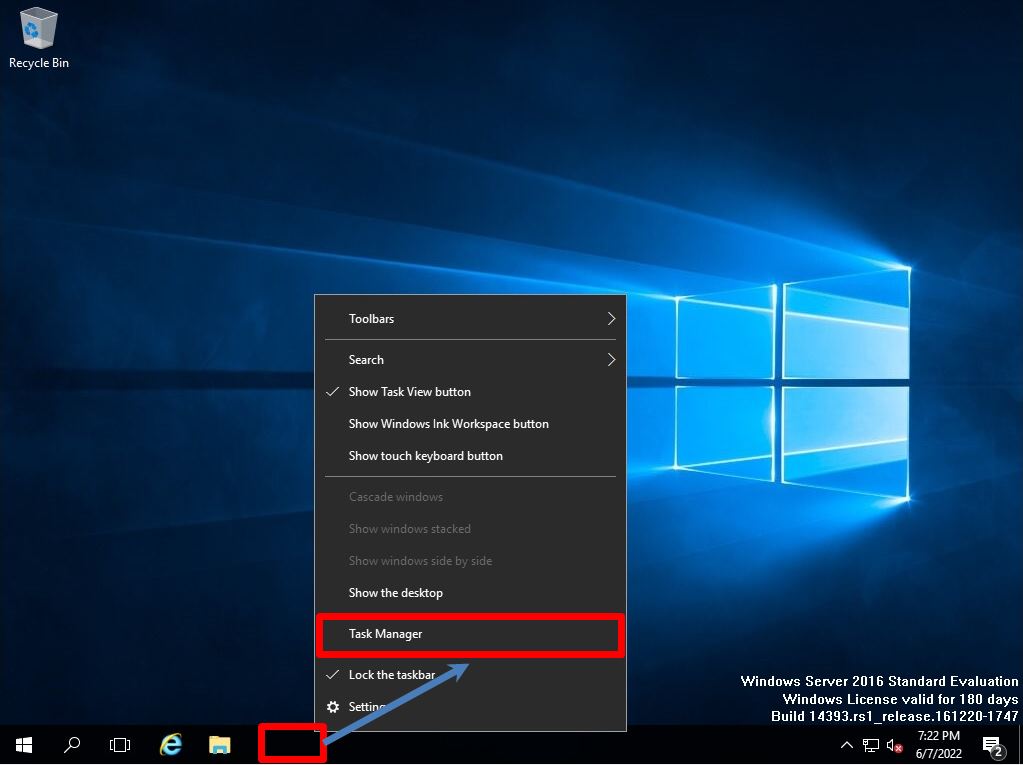
You can check the resource information of “CPU”, “Memory”, “Disk”, and “Network” on the “Performance” tab. * The disc is not displayed by default. It can be displayed by executing “diskperf -y” at the command prompt or PowerShell. To hide the disk, run “diskperf -n”.
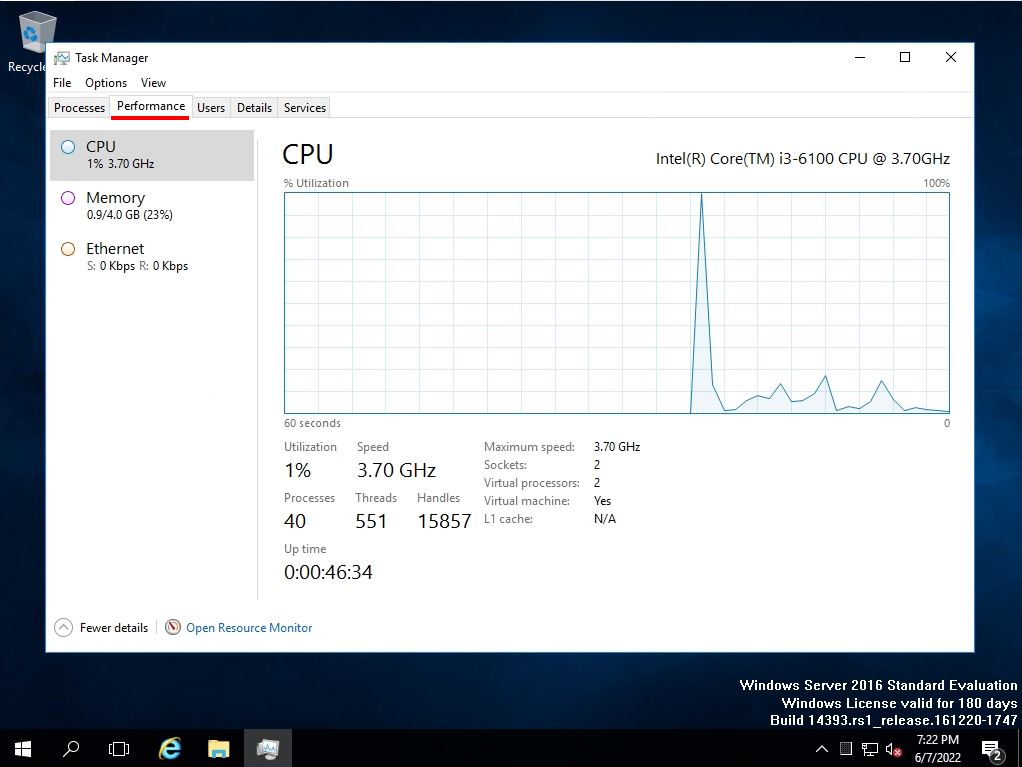
Command prompt-Task manager performance tab screen after executing “diskperf -y” in PowerShell. After executing the command as described above, you can display the disk items.